- The metaverse’s future lies in enterprise training, with sectors like healthcare and manufacturing realising real ROI through VR modules.
- Technologies like digital twins, generative AI, and secure blockchain credentials are driving immersive, hyper-personalised learning.
- While consumer adoption has lagged, enterprise use is accelerating, signalling a strategic shift from entertainment to mission-critical applications.
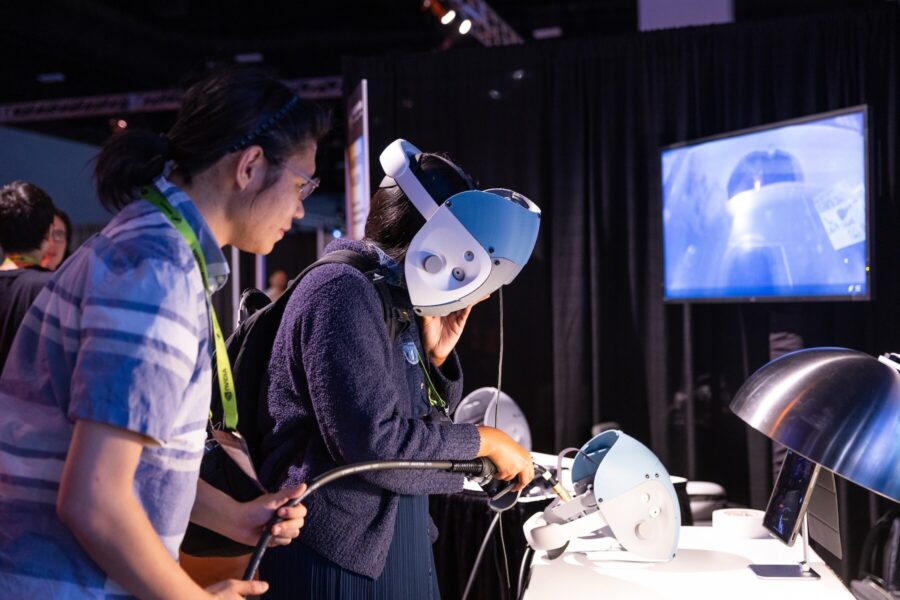
The metaverse, often heralded as the next frontier of digital interaction, has had a mixed reception. The commercial applications of the metaverse have, in consumer terms, decidedly not hit the mainstream, with much publicity on digital avatars, land sales, and huge financial losses for some tech giants. Behind the scenes, industries such as healthcare, law enforcement, and manufacturing are quietly adopting metaverse technologies, especially VR-based training modules, with actual tangible returns and measurable results.
This in itself is a powerful indicator of one crucial fact: that the metaverse’s long-term future will likely reside not in consumer entertainment but rather in purpose-built solutions serving specialised sectors, including corporate training and simulation. The question then shifts from “is the metaverse hype or reality?” to “are VR-based trainingmodules really getting adopted, and are they producing value?”
The Enterprise Shift: Beyond Consumer Fantasies
The struggles of the consumer metaverse, epitomised by Meta’s over $10 billion losses on AR/VR hardware, highlight its difficulty in finding mass appeal. However, enterprises are finding significant value in niche applications that solve real problems.
the above content looking smaller can u please edit this part
VR-Based Training: Tangible Returns and Widespread Adoption
ACSILabs is a pioneer in VR in the realms of manufacturing and law enforcement. In manufacturing, companies employ digital twins to simulate risky environments—jet engine tests at incredibly high altitudes, for example—with real-world tests being cut by 40% and prototype manufacturing from eighteen to just six months. This also rendered training for the new engineers complete in half the time.
In law enforcement, ACSILabs offers simulators for crisis response, from handling overdoses to armed standoffs, in risk-free virtual environments. A pilot study in 2025 indicated that VR-trained officers took 35% less time to make decisions, thereby boosting the readiness of officers at no more risk.
The application of these technologies arises from some key technological developments. Underpinning the metaverse are virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), extended reality (XR), and artificial intelligence (AI), all meant to provide the most immersive experience possible. These technologies empower learners or users to interact in real time with avatars in an environment that motivates and engages them.
n create metaverse experiences, along with “digital humans” who interact in a realistic manner.
Navigating the Challenges: Addressing the “Hype” Concerns
The gigantic promise of meta morphosis will surely usher in transformative educational and professional experiences so long as huge challenges are met and corrected in order to steer it from being just a hype. Privacy and security are at the forefront of concerns, with very sensitive biometric data being perhaps the most riveting: using VR headsets to collect such data wastes any chances of user trust if there is any noncompliance with laws such as the GDPR or HIPAA.
Another standoff is with legalities; if erroneous training in the metaverse results in an actual-world mistake, the question of liability arises. Such questions weigh heavily upon cases where international regulations disagree. Realistic simulations could be triggering for trauma or could perpetrate harassment under the guise of entertainment very reason we should have strong content moderation in place. Accessible means to enter the Metaverse are essential, but are too expensive, and still, very few have high-speed internet.
In 2023, UNESCO stated that 43% of learners globally do not possess consistent internet access. Educators also find the technical architecture of developing and running virtual environments a hard nut to crack: with 68% saying it was difficult to integrate VR in a 2024 survey. Consequent to the length of the VR session, users may experience motion sickness, eye strain, or disorientation, while social concerns like addiction and detachment from reality persist, especially for vulnerable users.
Putting it in another way, ethically, the metaverse risks deepening inequality by having only rich institutions purchasing premium hardware, while the mishandling of biometric information raises further concerns. Pedagogically, sceptics are wondering whether the metaverse logically offers anything or merely acts as eye candy without substantive frameworks for learning.
Finally, trust must be nurtured-the immersive platforms exacerbate emotional effects of abuses, scams, or intrusions. Without strategic planning and protections, the metaverse may fall on its own, adding to further scepticism and slowing down what should be a very potent learning and collaborative tool.
Investment and the Future of Corporate Metaverse Training
For investors, the enterprise metaverse, particularly in training and simulation, presents compelling opportunities. These include Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) leaders like Osso VR and ACSILabs, who build recurring revenue streams and benefit from high switching costs once integrated into workflows. Infrastructure providers like NVIDIA and Microsoft dominate the hardware and cloud infrastructure for the enterprise metaverse.
Additionally, specialized startups focusing on niche sectors like aerospace or law enforcement (e.g., ACSILabs) represent potential growth plays. The advice is clear: long-term hold for Microsoft and NVIDIA, and growth plays for Osso VR and ACSILabs (if listed), while generally avoiding consumer metaverse stocks unless they pivot to enterprise solutions.

PwC emphasises that the metaverse isn’t fully ready for “prime time” yet, but it can already create real business value today and position organisations for future reinvention. The guiding principle for managing metaverse risks and ensuring success is to design trust upfront and throughout the initiatives. This involves executive upskilling, creating specific risk taxonomies, and cross-domain collaboration.
The metaverse also holds potential as a force for good for environmental, social, and governance (ESG) initiatives, such as reducing carbon emissions through virtual meetings and fostering a more diverse and inclusive workforce by transcending geographic boundaries. However, this requires intentional design from the outset. The evolving nature of the metaverse also demands new, highly specialised skills for businesses, necessitating aggressive approaches to acquiring or cultivating talent.
Looking ahead, corporate metaverse training will experience further evolution. This is the time when analysts predict the rise of entry-level VR headsets by 2027. Hence, the technology will become more accessible. With 5G and eventual 6G network rollouts, the need and cost for local infrastructure will also lessen, in favour of gaining access to such services over inexpensive devices such as smartphones. For hyper-personalization regarding learning pathways, an AI will be able to factor into choices and be built around the needs of the individual as well as expertise.
Blockchain technology will also provide digital credentials that are secure and verifiable for training achievements. The metaverse will probably impact lifelong learning too, offering a virtual campus for professionals to be trained for real-world life skills from simulations. The actual metamorphosis into a hybridised way of learning (both brick-and-mortar plus virtual classrooms), specialising in courses and worldwide cooperation, is foreseen for 2035.
Conclusion
To conclude, while the consumer metaverse could have sputtered, enterprise adoption of VR-based training modules is gaining solid traction. This is not just a passing hype; it is a quiet revolution that generates real-world ROI, which manifests itself in better surgical outcomes, massive savings in manufacturing, and better decision-making in law enforcement.
Companies recognise its potential for onboarding, training, and process optimisation. Challenges do exist against this backdrop, pertaining to cost, privacy, technical barriers, and ethical considerations. These require strategic foresight and consideration to be implemented correctly, but the benefits and projections outweigh the challenges as the metaverse, for corporate training, is already a reality, “Beyond the Hype.”
The takeaway for businesses and investors is to disregard the consumer hype and focus on ROI-based solutions that will translate the benefits from virtual worlds to real-life advantages.
Quelle:
Foto: freepek